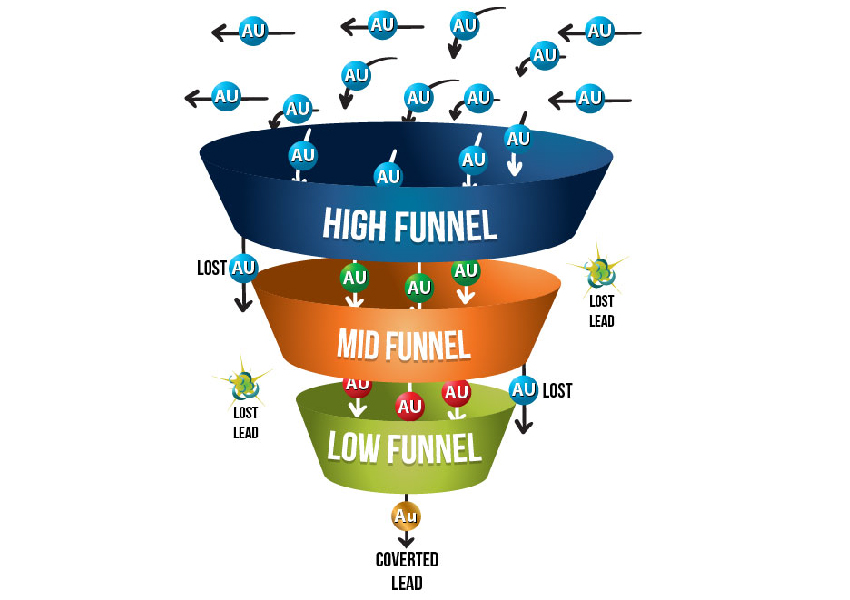
The sales funnel is an analogy that refers to the process that a customer goes through before they make a purchase and are “sold”. When a lead is generated through advertising, the marketing process, or even a face-to-face encounter, the lead turns into a prospective customer. At that point, the salesperson will designate that the prospect is “in the funnel”.
This is only the start of the transit of the lead through the sales funnel. The early funnel area is represented by the opening at the top, in the accompanying diagram.
Paid Search Sales Funnel Transit Time
Due to the average duration of the sales cycle (which varies dramatically depending on the type of product or service), sales or marketing professionals may expect how long it will take to turn a prospective customer into a booked sale. This “lead to sale” time is the average “funnel transit time”.
Leads coming in from search will move through different phases of consideration while in the funnel, deciding whether to purchase the product or service. During this process, some of them will “fall out” of the funnel and not lead to a sale. Not every lead entering a sales funnel will turn into a transaction. The desired outcome is usually to exit the funnel through a financial transaction, but completion of the funnel doesn’t always have to be financially motivated.
What happens inside a paid search sales funnel?
Before the arrival of digital marketing, the funnel might include a follow-up call from a salesperson to provide more information, looking to qualify the prospect further, or overcoming sales objections verbally.
Today, movement through a ppc sales funnel functions differently. It is a more independent process. It involves the prospective customer thinking the purchase through, doing some competitive shopping research, or perhaps just sitting on it for a while before making the decision.. These reasons are displayed in the diagram above.
Remarketing to prospects in the sales funnel
There are also proactive marketing processes that we can use in digital marketing. One of them is to remarket the prospect. Say perhaps you are selling cameras. The lead has studied some articles about the camera on your website and has become intrigued, and they fill out a form for information. Perhaps a few days later you show them a display ad from a display remarketing campaign and contact them via an email drip campaign.
Your remarketing list needs to be configured to not show ads too frequently, including to those who have already purchased a product or service i.e. those who have already converted. Instead, it should provide a gentle nudge and reminder to those still in the funnel that your site is a useful place to return.
Remarketing lists or “audiences” can be customized and shaped in several different ways to provide the most effective reminder.
Dynamic remarketing at the product level
In Google Shopping (e-commerce)we can generate dynamic product remarketing campaigns that operate at a product level.
With dynamic product remarketing, if someone has seen a product in a shopping campaign, an image and text ad can show up from a display campaign without the potential buyer even returning to the website. This is accomplished by linking a dynamic product remarketing campaign into the Google Shopping campaign’s Merchant Account and the associated product database.
Other methods of remarketing to the sales funnel
Traditional display remarketing campaigns are not product-specific. The variations of ways to remarket are endless including within search campaigns. For more information about using remarketing lists for search ads(RLSA) check out our search ads post as well!
Short Sales Funnels
Many businesses have rather short sales funnels like auto repair shops. Many auto repairs are not planned, a car breaks down, and the consumer may need it fixed quickly. So if they don’t already have a shop selected, or can’t get into their regular shop quickly, they’ll search for one, and the funnel can be completed within minutes.
Micro Conversion at funnel entrance.
Most sites can benefit from a “funnel entrance” or call to action. Typically this is accomplished by filling out a form (providing an email address) to obtain a useful white paper. This allows the site to remarket via email, entering that prospect into the funnel.
Freemium Sales Funnels
The freemium model that has become popular with internet-based companies, where you allow someone to use your product free for a trial period can be understood differently by looking at how it affects the funnel. The number of daily prospects exposed to freemium ads and movement through each funnel stage would be radically different. A freemium site would likely have a wider funnel entrance relative to the funnel exit, representing a lower success rate as leads move through the funnel.
Put numbers on it, and you can calculate ratios, percentages, and duration. For example, a non-freemium SAAS (software as a service) company with an application at a $40/mo price point might pull 1,000 prospects into their paid search sales funnel daily. If they offered a Freemium model, they might be converting 50 leads into free trials daily, depending upon the nature of their product, and the terms of their freemium offering. Their funnel transit time might be short, e.g. two days.
It is also important to note that freemium works differently depending on the product. A SAAS company with a monthly subscription service might have a funnel that looks quite different from a retailer’s.
Issues to consider with Freemium
There are some hidden operating costs in Freemium, for example, providing more pre-sale support to non-paying (trial) customers. This means that KPIs need to be identified, quantified, and understood for management to make the best decisions.
This might include the terms of their freemium models such as length of the trial, number of features/size of databases provided to Freemium-mode customers, and advantages or incentives given to people based upon the length of the sales contract.
All of this should be factored into a freemium business model to determine the impact on the sales funnel, and the total cost of ownership for the business.
Lead Handling and Sales Funnel Leakage
Sales objections typically are handled through e-mail or phone calls. In the case of phone calls, by using call tracking services and reviewing the recorded calls to our clients, we have pinpointed major problems with sales funnel lead handling. This can be a huge sales process choke point for many businesses. By understanding their sales funnel better, they can improve the phone call handling process, converting more prospects into sales.
An example of a sales funnel breakage/leakage point is a dentist who advertises for telephone call leads while their office is closed, then sends the prospect to voice mail. This practice will often result in losing 50-60% of people seeking dental treatment. It’s better to have a form to fill out with reassurance that you will call in the morning at the opening of business than to leave a disappointed caller. Or, at a minimum to have the voicemail system programmed to circumvent these types of issues.
The same type of problem is also encountered in large businesses, resulting in valuable leads being wasted. We have seen extreme examples of this in companies with $250 million and up in revenues.
Getting leads into the funnel
A major aspect that characterizes a successful sales funnel is that the leads behave like there is a powerful magnet pulling them in.
Some sales funnels are so powerful that anyone that gets near their entrance is effectively sucked in. Things like a free car being offered where only a hundred applicants are entered will have an incredibly high-interest rate and will be oversubscribed within minutes.
Other products have more narrow interest and in turn, are more narrowly targeted. It may take weeks to build a sizable sales funnel. They also depend on the scale of the business, their marketing strategy, how the product was positioned, what the competition looks like, and many other factors.
What kind of personas tend to be attracted into a sales funnel?
Each business has “a code to crack” to determine what the stages are in its sales funnel, how its target audience of buyers behave, and what helps address or overcome their concerns (‘sales objections’).
Often advertising tactics are used to pull prospects closer to the inlet of your funnel and then the real marketing heavy lifting is done when a well-engineered funnel is designed to overcome the most common sales objections inhibiting factors preventing a transaction. Sometimes it’s simple as time needs to lapse for people to consider a decision and a bigger purchase tend to have a longer sales cycle.
Using personas to develop a clearer understanding of a funnel
It is often helpful to create so-called ‘personas’ for your prospects, each representing the profile of an aggregate class of buyers. A business may typically have three to six personas who think and behave in similar patterns, but each could potentially become a converted prospect.
Until you understand a business’s personas, you can’t really understand the appropriate marketing process to make the sales funnel more efficient. Each business has a unique set of ‘buttons they need to push to help prospective buyers overcome their concerns and get the information they need to move towards the next step towards becoming customers.
Summary
The sales funnel is a powerful visual tool to represent what your potential buyers and customers are going through as they become aware of your products or services, and through the process of becoming paying customers.
The better you understand the sales funnel for your business, the more likely you’ll be able to succeed in creating a digital pipeline that moves the greatest percentage possible of suitable customers towards a transaction with your business.





